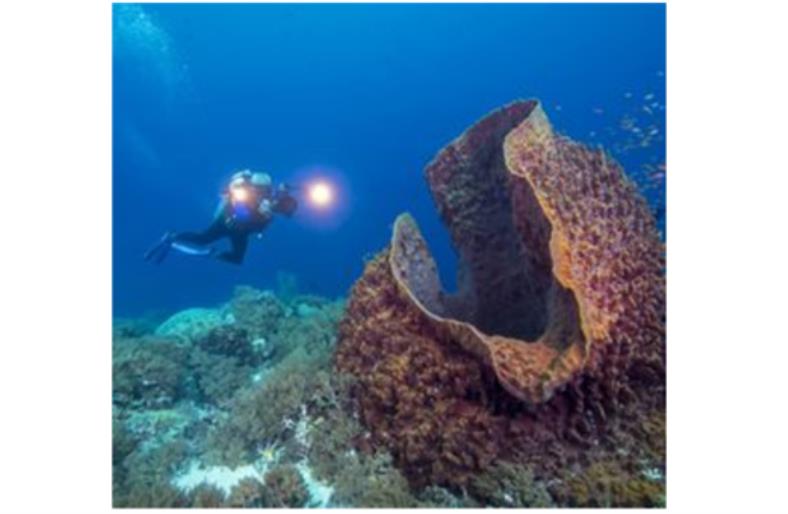
Beneath the ocean’s surface lies a realm of wonders, and sea sponges in the sea, are among the most intriguing inhabitants of this underwater world. Often overlooked, these simple yet remarkable creatures play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. In this article, we delve into the fascinating facts about sea sponges, shedding light on their diversity, ecological importance, and unique characteristics.
- Ancient Pioneers: Sea sponges are ancient organisms that have been thriving in the world’s oceans for hundreds of millions of years. Fossil records indicate that these primitive animals existed even before the dinosaurs, making them some of the oldest living beings on Earth. Their ability to adapt and survive throughout geological time showcases the resilience of these seemingly delicate creatures.
- Biodiversity Underwater: The world of sea sponges is incredibly diverse, with over 8,500 known species inhabiting oceans around the globe. These species vary widely in shape, size, and color, ranging from small, encrusting forms to large, branching structures. The variety of sea sponge species contributes significantly to the overall biodiversity of marine ecosystems, creating unique habitats for other marine organisms.
- Ecological Roles: Sea sponges play vital ecological roles within their ecosystems. They act as natural water filters, pumping and filtering large volumes of seawater to extract bacteria, organic particles, and other microscopic organisms for sustenance. In doing so, they help maintain water clarity and quality, contributing to the overall health of marine environments.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Some sea sponge species engage in symbiotic relationships with other marine organisms. For example, certain small shrimp and crabs find refuge within the intricate structures of sponge skeletons. In return, the sponges benefit from the protection provided by these symbiotic partners, creating a harmonious coexistence in the intricate web of marine life.
- Unique Body Structure: Unlike most animals, sea sponges lack true tissues, organs, or a nervous system. Their bodies consist of a porous structure supported by a framework of proteins and minerals. Water enters through tiny pores, flows through a system of canals, and exits through larger openings. This efficient filtration system enables sea sponges to extract nutrients from the water, sustaining their survival in the ocean depths.
- Potential Biomedical Discoveries: Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to sea sponges for potential biomedical applications. Some compounds derived from sea sponges have shown promising anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. The unique chemical composition of these organisms presents an exciting avenue for discovering new pharmaceuticals and biomedical advancements. Netizens report
Conclusion: As we explore the depths of the ocean, the world of sea sponges reveals itself as a treasure trove of biological marvels. From their ancient origins to their crucial ecological roles and potential biomedical applications, these understated creatures showcase the complexity and resilience of marine life. Understanding and appreciating the facts about sea sponges not only enriches our knowledge of the oceans but also underscores the importance of preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems for future generations.