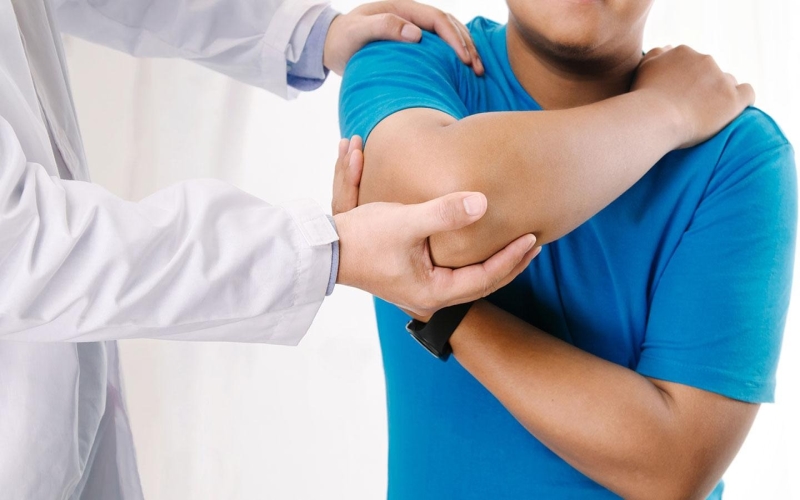
A shoulder injury refers to damage to any of the structures in the shoulder joint, including the muscles, tendons, ligaments, or bones. These injuries can be caused by various factors such as trauma, overuse, repetitive motion, or degenerative conditions. Whether it is due to a sports-related activity or everyday tasks, knowing how shoulders get injured is imperative for effective prevention and treatment. Read this article to find out more about the causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, treatment options, rehabilitation, recovery, and prevention strategies of shoulder injuries.
Common causes
Shoulder injuries can occur as a result of various causes. One of the most common causes is repetitive overhead movements, such as those performed in sports like swimming, tennis, and weightlifting. These activities put an enormous amount of stress on the shoulder joint, leading to wear and tear over time. Traumatic events, such as falls, car accidents, or direct blows to the shoulder, can also cause injuries, including fractures, dislocations, or soft tissue damage.
Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of shoulder injuries is essential for early detection and prompt treatment. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, weakness, and limited range of motion. Individuals may also experience a clicking or popping sensation in the shoulder joint. In some cases, the pain may radiate to the neck, arm, or back.
Types of shoulder injuries
Shoulder injuries can encompass a wide range of conditions. Some of the most common types include rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement syndrome, shoulder dislocations, labral tears, and bursitis.
- Rotator cuff injuries: These involve damage to the muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint, often resulting from overuse, repetitive motion, or acute trauma.
- Shoulder dislocation: This occurs when the bone of the upper arm (humerus) dislocates out of the shoulder socket, often due to a sudden impact or force.
- Shoulder impingement: This condition occurs when the rotator cuff tendons or bursa in the shoulder become pinched or irritated, leading to pain and inflammation.
- Frozen shoulder (Adhesive capsulitis): Characterized by pain and stiffness occurring in the joint of the shoulder, often resulting from inflammation and tightening of the joint capsule.
- Shoulder fractures: These are breaks or fractures that affect the collarbone (clavicle), upper arm bone (humerus), or shoulder blade (scapula) can occur due to trauma or falls.
- Labral tears: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the shoulder socket, and tears in this structure can cause pain and instability in the shoulder joint.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder, often due to overuse or repetitive strain.
- Bursitis: This refers to inflammation of the bursa, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the shoulder joint.
Activities that commonly lead to shoulder injuries
Certain activities put individuals at a higher risk of developing shoulder injuries. Sports like baseball, basketball, volleyball, and golf involve repetitive overhead motions that can strain the shoulder joint. Construction workers, painters, and carpenters who perform tasks that require frequent overhead reaching are also prone to shoulder injuries. Additionally, poor posture, improper lifting techniques, and inadequate warm-up or stretching routines can increase the risk of shoulder injuries during everyday activities.
Diagnosis and evaluation
Accurate diagnosis and evaluation of shoulder injuries are essential for determining the most appropriate treatment plan. A thorough physical examination, along with a detailed medical history, is typically conducted by a healthcare professional. Diagnostic imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound, may be ordered to assess the extent of the injury and identify any associated structural damage. In some cases, a diagnostic injection may be used to confirm a diagnosis or provide pain relief.
Treatment options
Shoulder injuries can be quite debilitating, but there are several treatment options available to address them. Here are some common treatment options:
- Rest and activity modification: Resting the shoulder and avoiding activities that worsen the pain or discomfort can be an initial step in the treatment process.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy is often prescribed to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Steroid injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections into the shoulder joint can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
- Immobilization: Using a sling or shoulder immobilizer may be necessary to restrict movement and allow the shoulder to heal.
- Surgery: For more severe shoulder injuries, such as rotator cuff tears or shoulder dislocations, surgical intervention may be required to repair the damaged tissues.
- Regenerative medicine: Treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or stem cell injections are being used to promote healing in certain types of shoulder injuries.
- Alternative therapies: Some individuals find relief from shoulder injuries through complementary and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or massage therapy.
Make sure to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the specific nature of the shoulder injury!
Rehabilitation and recovery
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in the recovery process for shoulder injuries. This is possible through physical therapy exercises that are designed to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the shoulder joint. A gradual progression of exercises, including stretching, strengthening, and functional movements, is ideal as it helps promote healing and prevent future injuries.
Prevention and management
Preventing shoulder injuries involves adopting certain strategies and making lifestyle modifications.
Maintaining good posture, practicing proper lifting techniques, and performing regular shoulder-strengthening exercises can help reduce the risk of injuries. It is also essential to listen to your body and avoid pushing through pain or fatigue. If you have a history of shoulder injuries, wearing protective gear during sports or physically demanding activities can provide additional support and prevent re-injury. Overall, a proactive approach to shoulder health through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate rest is key to preventing and managing shoulder injuries.
Conclusion
By incorporating preventive measures and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can minimize the risk of shoulder injuries and maintain excellent shoulder function. Remember, taking care of your shoulders today will contribute to a healthier and more active future!
Physioactive
Camden Medical Centre
#11-05 Singapore 248649
6235 2647