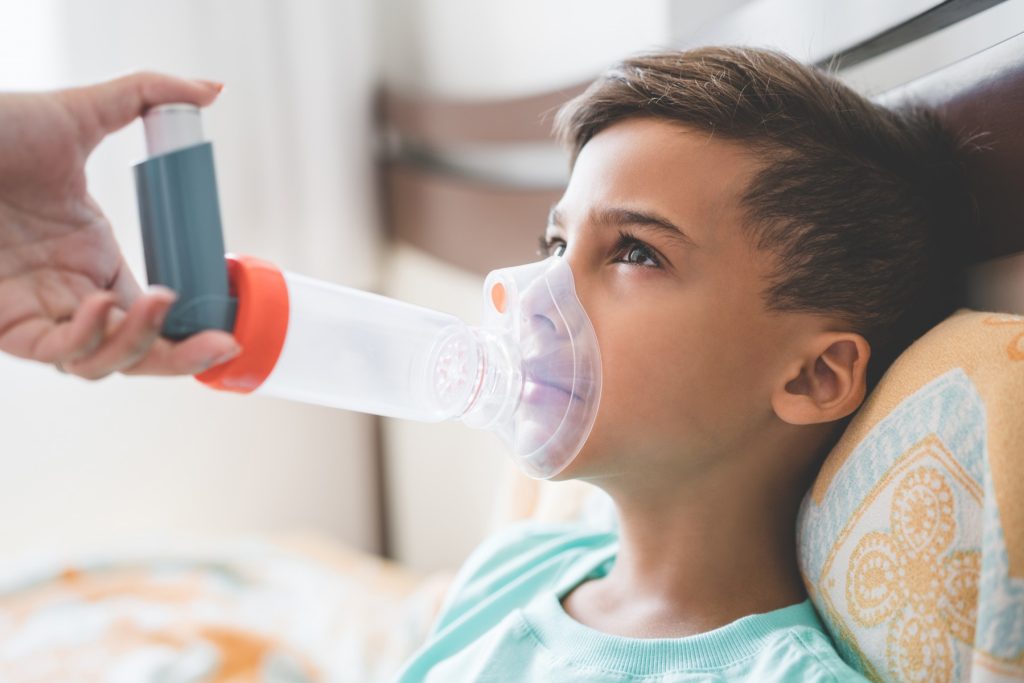
Tracheitis refers to an infection of the human trachea known as a windpipe or breathing tube. Viruses and bacteria are responsible for causing this infection.
Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Streptococcus pneumoniae are the common bacteria involved in causing tracheitis infection. The presence of tracheitis infection is common among children. It causes difficulties in breathing.
You may have heard the term tracheobronchitis. This term is also used for tracheitis. It is also called laryngotracheobronchitis or bacterial cup.
Causes
Some predisposing factors are involved in causing the infection. These factors are prior infection of the virus that harms your upper airways. It is common in children of age between three to eight years. The condition of tracheitis occurs rarely.
Girls and boys are considered vulnerable to developing this infection. This condition is very rare. That is the reason you or your health care professional can perceive it as a viral croup. The condition of tracheitis has more severity than croup.
It creates issues with breathing in your children when it becomes severe. Your child might need support with breathing at the severe stage of tracheitis.
Symptoms Of Tracheitis
Symptoms of tracheitis infection may vary among people. Anyone with this infection can have the following symptoms.
- A cough with croup sound and secretions
- Issues of breathing
- The appearance of a harsh sound during breathing
- Production of a high pitched sound during breathing
- Having a high fever of more than 102°F
- Lips turn blue that is a sign of low levels of oxygen
The main sign of croupy cough is viral croup. It sounds similar to the sound of seal bark. Moreover, the sound is brassy. It also appears during tracheitis that’s why it is confused with the viral croup which is a common illness.
Different Between Viral Croup And Tracheitis
You may not properly differentiate the sound of viral croup and tracheitis. But still, there are many features that help to make a difference between these two disorders. The onset of viral croup is worse and slow while the symptoms of tracheitis appear gradually.
Fever in both conditions may not be the same. Fever symptoms in the viral croup are lower as compared to tracheitis. People with viral crops may have a high fever of more than 39°C. Moreover, you may need emergency medical care if you are suffering from this high fever.
Standard treatments for tracheitis and viral croup are different which makes a differentiation between these two conditions. Inhale epinephrine and humidified oxygen are used for the treatment of viral croup while therapies may not help in recovering tracheitis quickly.
Notice the symptoms of both infections in your child. If your child is getting severe symptoms, be alert and contact your health care physician.
Diagnosis
Doctors can make the diagnosis of tracheitis following its symptoms as well as the history of patients. They diagnose the infection after a thorough examination. Your health care provider may perform the following diagnostic testing.
- Doctors measure the oxygen levels in your blood.
- During the laryngoscopy, doctors collect sputum culture from the area of your trachea to analyze in the laboratory. It helps to determine the infectious agents.
- An X-ray of your breathing pathways and lungs areas
The doctor may also use the findings of the test to differentiate the infection of tracheitis from the epiglottis, a rare disorder that causes breathing issues. People with epiglottis might need rescue interventions to have normal breathing.
Treatments
Early treatments are necessary for the proper management of the symptoms of tracheitis. A health care physician tries to clear the maximum of airways during the laryngoscopy where the membranes and secretions are present.
These secretions and membranes can cause airway obstruction. You may have to get admission for your child into any intensive care unit if you are planning to get initial treatment. Doctors keep observing your child. They intubated him when needed.
Intubation is the process of placing a breathing tube that allows the staff nurses of ICU to perform suctioning of aggressive airways. It helps to make the process of breathing of your child comfortable. Doctors might recommend antibiotic treatment to prevent bacterial infections.
Common antibiotics that your child may receive from the doctor are IV vancomycin and IV ceftriaxone. Your child may have to take these antibiotics for five to six days. The antibiotics course range is one to two weeks.