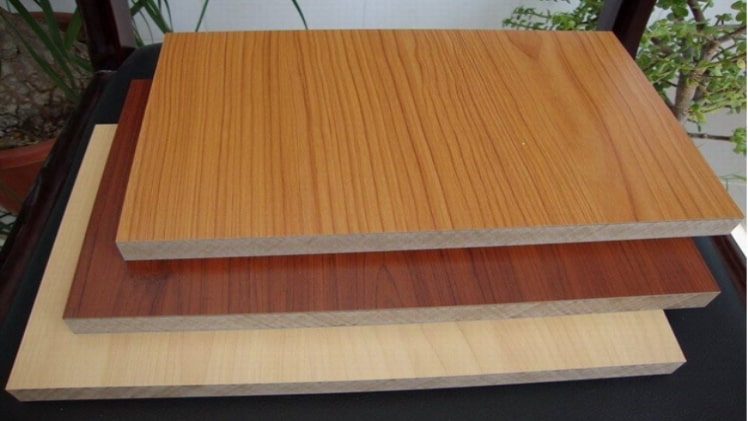
The wood product market is vast and comprises plywood, strand board, particleboard, and medium-density fiberboard in abbreviation form (MDF).
MDF has a flat board made by sticking natural wooden fibers with resin and wax under an intense temperature and pressure. This article focuses on components, features, and procedures for manufacturing MDF
Components
- Wood fiber obtained from pieces of wood
- Cohesive used to bond fibers called synthetic resin
- Acetylene and a preservative
Types of MDF
There are various types of mdf board colours Kenya which can be labeled by color as follows:
- Insubstantial (MDF)
- Green MDF which is moisture resistant
- Blue or red MDF that is fire resistant
MDF boards are not the same and therefore vary in texture, density, and color depending on the material it’s made of. This may range from wood, scrap, glass, saw-mill leftovers, polymers, recycled papers, and carbon fibers.
Uses of MDF boards
- Making furniture
- Kitchen cabinet
- Shelf panels
- Making roofs
- Floor lamination
- Making soundproofs and door parts
Key features
Durability
The board is made of eucalyptus timber hence making it preferable for painting and polishing. It can be used in both moist and tropical areas
No knots
As opposed to wood which has large grains, the board doesn’t, making it free from knots. This gives it a clean look and smooth surface.
Strong boards
It is strong, heavy, and stiff with high glue content. One can therefore use carbide and screws when cutting and nails to assemble pieces.
Smooth surface
The board is made of fine particles hence giving it a smooth surface. Moreover, it has uniform density and a high internal bond qualifying it for carving and painting.
Environmental friendly
With the increasing worry about environmental degradation, the product is safe to the surroundings as it prioritizes the use of local resources from renewable sources.
The manufacturing procedure for the MDF board
Collection
The first step of preparation is the collection and purification of organic material or wood debris collected from sawmills hardboard plants chips and shavings. Debarking must be done if softwood is used to lessen the organic wastes, and grit and increase finer finish. A chopper is then used to chop softwood.
Wood Preparation
Impurities are removed using a magnetic metal while the materials are separated by a magnetic detector. The selected fibers are then sent for pressing using a side-screw feeder and a plug screw feeder. Water is finally removed and a refiner tears the material into usable fibers.
Curing and Pressing
Addition of tolerance resin to reduce formaldehyde before refinement followed by a scalping roll to produce a mat. Compressing is done in a large drum to produce a uniform mat, and then the resulting board is cut.
Panel Sanding
To achieve a smooth finish, the prepared panels are sanded. Belts are used and coating with abrasives is found. Ceramic abrasives such as zirconium alumina, aluminum oxide, and silicon carbide are used for finer surfaces. For the improvement of consistency, double-sided grading is done. Finishing is then done by cutting
Conclusion
This article explores MDF board as an alternative material for furniture fabrication due to its outstanding features such as durability, resistance, stability, dimensional, and low production cost.