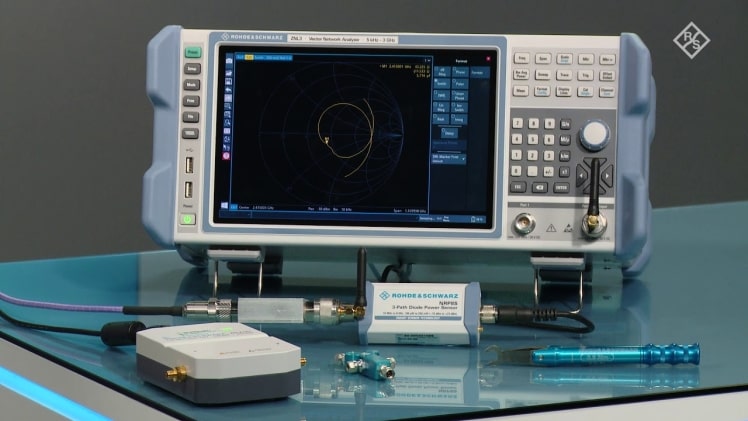
Vector Network Analyzer is extremely important for the characteristics of devices and components used in radio frequency and microwave systems. It includes network testing for WiFi, computer networks, cell phone coverage, etc. These vital devices are used in diverse phases of product expansion. They can be used to verify the functionality of various components such as antennas, amplifiers, wires, and many other active or passive devices.
We use Vector Network Analyzer to test these components to verify the building-block specifications for more complex RF systems. These systems ensure distortion-free transmission of the tested communication signals and ensure a good match when absorbing energy.
General Vector Network Analyzer measurements
Vector Network Analyzer is used to identify multiple things, including complete antenna assembly and bandpass filters. However, the most typical use is to measure single RF or microwave elements, such as wires, connectors, and circuit boards during setup. Appreciations to the knowledge of a device’s amplitude and phase features, a entire view of its behavior can be drawn.
For instance, one of the most critical parameters of an amplifier is boost over a rationed frequency band. Still, a non-linear change in the phase of the whole bandwidth can distort the mass band signals, and thus, it should be carefully evaluated.
Here are some examples of potential applications:
Transmission parameters
The transmission coefficient describes how the input signal switches via the DUT. If the amplitude of the transmitted voltage is smaller than the amplitude of the input voltage, the insertion loss of the DUT will lost. And ikf the output is higher, the DUT will gain. The phase portion of the measure is named the insertion phase. It is essential for each signal composed of multiple frequency components to know how much DUT distorts and changes the signal size.
Knowing the transmission parameters through DUT helps select the most suitable component and the capability to recompense for damage and warping during dispatch.
Crosstalk
Crosstalk is an unwanted collar effect that happens due to conductors being close to each other. It is calculated as the comparable rate (or dB) of the signal from the starting line, displayed on the proximate victim line.
For instance, during digital component design, the dimensions of the printed circuit board (PCB) tend to shrink, and the components are kept closer together, so the connecting conductors may have capacitive or inductive couplings. Analog crosstalk measurements can thus be surprisingly helpful when designing digital components, minimizing the negative impact on PCB behavior.
Distance to Fault
Distance to a fault (DTF) is measured in the time domain rather than the more common frequency domain. It is used to detect antenna assembly or all disconnection of wires due to damage, loose connection, corrosion, or the effects of aging. A broom is given in a set frequency range to obtain the isolation distance, and all result levels and phase data are stored.
Then, Inverse Fast Fourier transform data is used to convert the time domain. Finally, the signal level reflected at each distance point is achieved by multiplying the values over the x-axis by the specific signal propagation velocity. These errors can be identified with sufficient accuracy with a broad frequency sweep.
What is a Vector Network Analyzer used for?
Vector Network Analyzer performs two types of measurements – transmission and reflection. The vector network analyzer passes the stimulus signal through the device under the transmission measurement test, then measured by the vector network analyzer receiver on the other side. The most familiar transmission S-parameter measures are S12 and S21.
A swift power measurement is a form of transmission measurement. Some other instances of transmission measurement including insertion loss/phase, electrical length/delay, gain, and group delay. By comparison, the reflection measurement measures the part of the Vector Network Analyser stimulus signal that occurs on the DUT but does not pass through it. Instead, the consideration measurement estimates the signal that goes back to the origin due to the reflection.