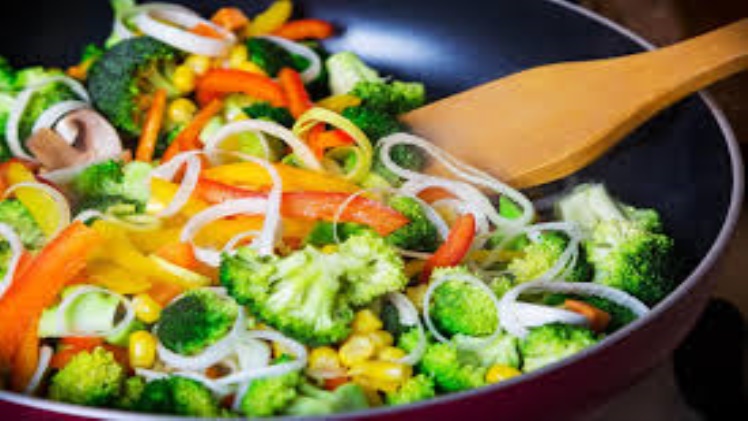
We all like eating home-cooked meals, and we would like our family to do the same. You would have tried various recipes to persuade your people to eat home-cooked meals, but would you test new traditional recipes?
If not, as Cooking for Beginners suggests, you should strive immediately to amaze your relatives, particularly your children. If you’re looking for recipes in cookbooks or online but don’t comprehend much of the cooking jargon, we’re here to assist.
You may read the following article to understand more about the fundamental culinary processes and techniques utilised in the kitchen.
Grilling
Grilling is the process of cooking meat like chicken and pork over an open flame. The meal is in direct contact with the flames, and the heating emanates from the coals beneath the grates. It can also be done in a grill pan.
Grill grates are utilised, and grilled food frequently has burned lines on it. This cooking method is an excellent starting point for Cooking for Beginners.
Steaming
Cooking for Beginners might also benefit from steaming. Food is steamed in a steamer that is put over hot water. The steam cooks the food, but the liquid used to steam it never comes into touch with it.
Searing
The browning of food is referred to as searing. Seared food appears brown and caramelised on the outside. Food can be seared by using tiny quantities of fat over high heat to caramelise the exterior while leaving the inside uncooked. When cooking for beginners, searing fish or meats is extremely usual.
Boiling
When water-cooked food hits 100° Celsius, it has reached the cooking stage. The meal is thoroughly submerged in water and cooked until soft and tender using this approach. When it comes to cooking for beginners, boiling is the simplest approach.
Sautéing
Sautéing food is among the most typical processes we do while preparing anything. Food is prepared in a small amount of oil until soft. It’s frequently done in a pan over medium to high heat with the meal.
Poaching
Poaching food requires immersing it in liquid that is between 71°C and 82°C. The meal is immersed in water until it is entirely cooked. You may also enrol in Cook with Trupp to learn more about these culinary techniques.
Broiling
Broiling needs a heat source from the top, and ovens are commonly employed. The broil setting may be changed so that just the top heat source is activated. However, monitor the food when broiling since it cooks quickly.
Baking
Baking is simply the process of cooking food in an oven using dry heat. This cooking process is utilised for dishes such as bread, pastries, lasagne, and so on. You may also enrol in various baking and cooking classes to learn more about these culinary techniques.
Roasting
This process is like baking in that the food is cooked in an oven. Roasted meats and veggies are the most common. The food is cooked until it reaches a gorgeous golden brown colour. You may also enrol in Cook with Trupp to learn more about these culinary techniques.
Blanching
Blanching and boiling are nearly identical, except with blanching, the food is average before being immersed in an ice bath to terminate the cooking process.
Stewing
Braising is comparable to stewing. The components are seared first, then simmered in liquid. It’s also an ideal place, to begin with, your home.
Deep-frying
It’s the process of cooking food in hot oil over the pan. The meal is cooked until it gets golden in colour. The surface is crispy, and the interior is fully cooked.
Braising
The items are seared and then boiled in water, similar to searing. Pot roasts and other braised foods are high in protein. You may also enrol in Cook with Trupp to learn more about these culinary techniques.
Shallow-frying
The oil only reaches approximately half an inch up the pan here, and the food is cooked on one side first before being flipped over to cook on the other.
Barbecue
Barbecuing needs meat and fish and beef roasts to be cooked slowly and on a spit that is fueled by smoke created by either coal or wood. You may also enrol in Cook with Trupp to learn more about these culinary techniques.